Difference between revisions of "Basic electricity:1.5 Resistance"
m (Admin moved page Basic electricity:Resistance to Basic electricity:1.5 Resistance) |
|||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
= {{PAGENAME}} = | = {{PAGENAME}} = | ||
A third factor that plays a role in an electrical circuit is resistance. All material impedes the flow of electrical current to some extent. The amount of resistance depends upon composition, length, cross-section and temperature of the resistive material. As a rule of thumb, resistance of a conductor increases with an increase of length or a decrease of cross-section. Resistance is designated by the symbol "R". The unit of measurement for resistance is ohms (Ω). | Resistance is defined as the property of a substance due to which it opposes (or restricts) the flow of electricity (i.e., electrons) through it. | ||
A third factor that plays a role in an electrical circuit is resistance. All material impedes the flow of electrical current to some extent. The amount of resistance depends upon the composition, length, cross-section, and temperature of the resistive material. As a rule of thumb, the resistance of a conductor increases with an increase of length or a decrease of the cross-section. Resistance is designated by the symbol "R". The unit of measurement for resistance is ohms (Ω). | |||
== Resistance circuit symbols == | == Resistance circuit symbols == | ||
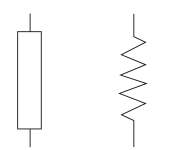
[[File:Resistance.png|right|Resistance symbol|class=img-box]]Resistance is usually indicated symbolically on an electrical drawing | [[File:Resistance.png|right|Resistance symbol|class=img-box]]Resistance is usually indicated symbolically on an electrical drawing in one of two ways. An unfilled rectangle is commonly used. A zigzag line may also be used. | ||
Resistance can be in the form of various components. A resistor may be placed in the circuit, or the circuit might contain other devices that have resistance. | Resistance can be in the form of various components. A resistor may be placed in the circuit, or the circuit might contain other devices that have resistance. | ||
Revision as of 03:20, 13 February 2022
1.5 Resistance
Resistance is defined as the property of a substance due to which it opposes (or restricts) the flow of electricity (i.e., electrons) through it.
A third factor that plays a role in an electrical circuit is resistance. All material impedes the flow of electrical current to some extent. The amount of resistance depends upon the composition, length, cross-section, and temperature of the resistive material. As a rule of thumb, the resistance of a conductor increases with an increase of length or a decrease of the cross-section. Resistance is designated by the symbol "R". The unit of measurement for resistance is ohms (Ω).
Resistance circuit symbols
Resistance is usually indicated symbolically on an electrical drawing in one of two ways. An unfilled rectangle is commonly used. A zigzag line may also be used.
Resistance can be in the form of various components. A resistor may be placed in the circuit, or the circuit might contain other devices that have resistance.
Units of measurement for resistance
The following chart reflects special prefixes that are commonly used when dealing with values of resistance:
| Prefix | Symbol | Decimal |
|---|---|---|
| 1 kiloohm | 1 kΩ | 1000 Ω |
| 1 milliohm | 1 mΩ | 1/1000 Ω |
| 1 microohm | 1 μΩ | 1/1,000,000 Ω |