Difference between revisions of "Basic electricity:2.1 Ohm's Law"
(Created page with "= {{PAGENAME}} =") |
|||
| (One intermediate revision by the same user not shown) | |||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
= {{PAGENAME}} = | = {{PAGENAME}} = | ||
== George Simon Ohm and Ohm's Law == | |||
The relationship between current, voltage and resistance was studied by the 19th-century German mathematician, George Simon Ohm. Ohm formulated a law that states that current varies directly with voltage and inversely with resistance. From this law the following formula is derived: | |||
:: <math> {current} = {{voltage} \over {resistance}}</math> | |||
or | |||
:: <math> I = {E \over R}</math> | |||
Ohm's Law is the basic formula used in all electrical circuits. Electrical designers must decide how much voltage is needed for a given load, such as computers, clocks, lamps and motors. Decisions must be made concerning the relationship of current, voltage and resistance. All electrical design and analysis begins with Ohm's Law. There are three mathematical ways to express Ohm's Law. Which of the formulas is used depends on what facts are known before starting and what facts need to be known. | |||
:: <math> I = {E \over R}</math> | |||
:: <math> R = {E \over I}</math> | |||
:: <math> E = {I \times R}</math> | |||
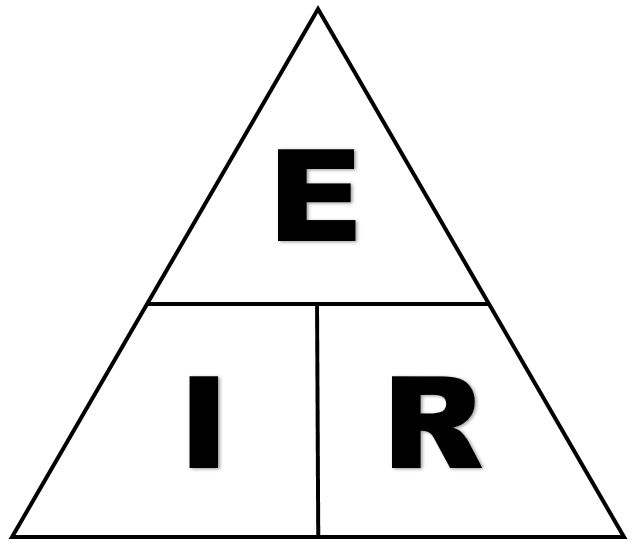
== Ohm's Law triangle == | |||
There is an easy way to remember which formula to use. By arranging current, voltage and resistance in a triangle, one can quickly determine the correct formula. | |||
[[File:Ohm%27s_Law.jpg|center|Ohm's Law Triangle|class=img-box]] | |||
Latest revision as of 04:14, 30 December 2021
2.1 Ohm's Law
George Simon Ohm and Ohm's Law
The relationship between current, voltage and resistance was studied by the 19th-century German mathematician, George Simon Ohm. Ohm formulated a law that states that current varies directly with voltage and inversely with resistance. From this law the following formula is derived:
or
Ohm's Law is the basic formula used in all electrical circuits. Electrical designers must decide how much voltage is needed for a given load, such as computers, clocks, lamps and motors. Decisions must be made concerning the relationship of current, voltage and resistance. All electrical design and analysis begins with Ohm's Law. There are three mathematical ways to express Ohm's Law. Which of the formulas is used depends on what facts are known before starting and what facts need to be known.
Ohm's Law triangle
There is an easy way to remember which formula to use. By arranging current, voltage and resistance in a triangle, one can quickly determine the correct formula.